In today’s digital landscape, safeguarding personal information is paramount. Device encryption serves as a crucial defense against unauthorized access, protecting sensitive data from prying eyes. This guide provides a comprehensive understanding of device encryption across various operating systems, empowering you to enhance your digital security posture. We’ll explore different encryption methods, their strengths and weaknesses, and provide clear, step-by-step instructions for implementation and management.
From understanding the basics of encryption to mastering the intricacies of password management and regular system updates, we aim to equip you with the knowledge necessary to confidently protect your valuable data. Whether you’re a tech novice or a seasoned user, this guide offers practical advice and actionable steps to bolster your device’s security.
Understanding Device Encryption
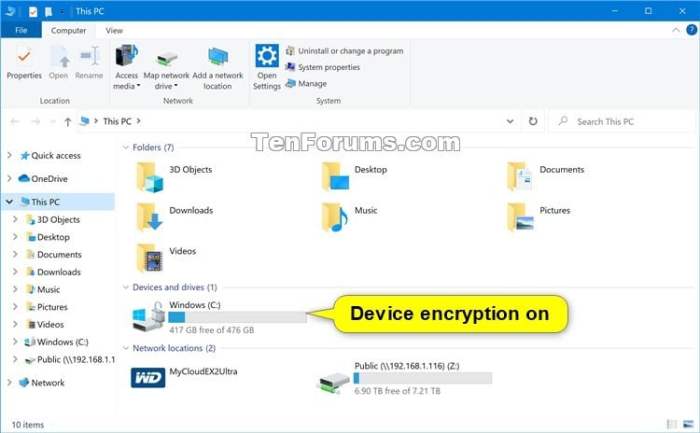
Device encryption is a crucial security measure that protects your personal data by scrambling it into an unreadable format. This prevents unauthorized access to your files, photos, messages, and other sensitive information, even if your device is lost, stolen, or compromised. Different operating systems offer varying approaches to encryption, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these differences is vital for making informed decisions about securing your digital life.
Device Encryption Methods Across Operating Systems
Android, iOS, Windows, and macOS each employ different encryption methods, offering varying levels of security and performance trade-offs. Android devices typically utilize full-disk encryption, encrypting all data stored on the device’s internal storage. iOS devices also employ full-disk encryption by default. Windows offers BitLocker (for Pro and Enterprise editions) which provides full-disk encryption, while File Encryption is available for all versions.
macOS uses FileVault, a full-disk encryption system.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Device Encryption
The primary benefit of device encryption is enhanced data security. Encrypted data is essentially useless to anyone without the correct decryption key, significantly reducing the risk of data breaches. However, encryption can introduce a performance overhead, potentially slowing down boot times and application performance. The degree of this slowdown varies depending on the encryption method, the device’s hardware capabilities, and the amount of data being encrypted.
Another potential drawback is the accessibility aspect. If you forget your decryption key or password, you might lose access to your data entirely. This highlights the importance of choosing a strong, memorable password, and potentially using a password manager.
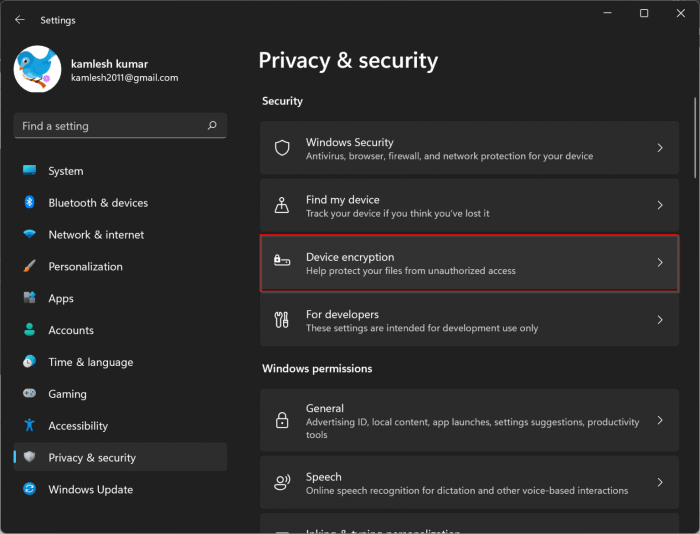
Checking for Existing Encryption
To check if your device is already encrypted, follow these operating system-specific instructions:
Android
- Open the Settings app.
- Tap Security or Security & location.
- Look for an option related to Encryption or Screen security. The exact wording may vary depending on your Android version and device manufacturer. The presence of an encryption setting usually indicates that encryption is enabled.
iOS
- Open the Settings app.
- Tap Face ID & Passcode (or Touch ID & Passcode on older devices).
- Scroll down and check for the ” Data Protection” setting. This setting is usually already enabled by default.
Windows
- Open the Control Panel.
- Go to System and Security.
- Click on BitLocker Drive Encryption. If this option isn’t present, your edition of Windows may not support BitLocker. You can check for File Encryption instead, often found within the same menu.
macOS
- Click the Apple menu in the top-left corner of your screen.
- Select System Preferences.
- Click on Security & Privacy.
- Select the FileVault tab. If FileVault is on, it indicates that your drive is encrypted.
Comparison of Encryption Methods
| Operating System | Encryption Method | Security Level | Performance Impact | Ease of Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Android | Full-disk encryption (varies by manufacturer and Android version) | High | Moderate | Moderate |
| iOS | Full-disk encryption (default) | High | Low to Moderate | High |
| Windows | BitLocker (full-disk), File Encryption | High (BitLocker), Moderate (File Encryption) | Moderate (BitLocker), Low (File Encryption) | Moderate (BitLocker), High (File Encryption) |
| macOS | FileVault (full-disk) | High | Moderate | Moderate |
Enabling and Configuring Device Encryption

Enabling device encryption adds a crucial layer of security to your data, protecting it from unauthorized access even if your device is lost or stolen. This process involves encrypting the entire storage drive, meaning all files and data are scrambled and unreadable without the correct decryption key (your password or passphrase). The specific steps vary slightly depending on your operating system, but the core principles remain consistent.Enabling full-disk encryption requires careful consideration and understanding of the implications.
Once enabled, accessing your data requires entering the correct password or passphrase; forgetting it could result in permanent data loss. Therefore, choosing a strong and memorable password is paramount.
Enabling Full-Disk Encryption on Different Operating Systems
Different operating systems offer varying methods for enabling full-disk encryption. Windows utilizes BitLocker, macOS employs FileVault, and Linux distributions typically use tools like LUKS (Linux Unified Key Setup). Each system presents a unique interface and configuration process, requiring users to follow the specific instructions provided within their operating system’s settings. For example, on Windows, BitLocker can be activated through the Control Panel, while on macOS, FileVault is accessible through System Preferences.
Linux distributions often require using the command line interface for encryption management. Consulting the official documentation for your specific operating system is essential for accurate and safe implementation.
Setting a Strong Encryption Password or Passphrase
Choosing a robust password or passphrase is critical for the effectiveness of your device encryption. A weak password can be easily cracked, rendering your encryption useless. Best practices recommend using a passphrase that is at least 16 characters long, combining uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid using easily guessable information such as birthdays, names, or common words.
Consider using a passphrase generator to create a strong, random passphrase and storing it securely, perhaps using a password manager. Remember, this password is the key to your encrypted data; its security is paramount.
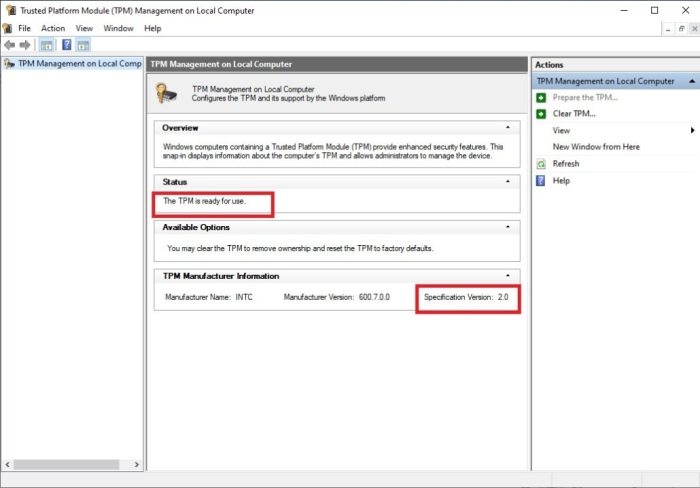
Implications of Forgetting Your Encryption Password and the Recovery Process
Forgetting your encryption password can lead to irreversible data loss. Without the correct password, accessing your encrypted data is impossible. While some operating systems offer recovery options, such as a recovery key or a trusted platform module (TPM), these mechanisms are not foolproof. The recovery process can be complex and time-consuming, and in some cases, data recovery might not be possible.
Therefore, it is crucial to store your encryption password securely in a safe and accessible place, ideally separate from your device, while ensuring it remains confidential.
Enabling and Configuring Device Encryption on Android
The following flowchart illustrates the steps involved in enabling and configuring device encryption on an Android device.
Managing and Maintaining Device Encryption
Maintaining strong device encryption is an ongoing process, not a one-time task. Regular attention to your encryption settings and related security practices is crucial to ensure your data remains protected. Neglecting these aspects can leave your sensitive information vulnerable to theft or unauthorized access.Device encryption, while highly effective, is only as strong as its weakest link. This means that weak passwords, outdated operating systems, or improperly configured settings can significantly undermine the security provided by encryption.
Understanding the potential risks and implementing robust maintenance strategies is therefore essential.
Risks Associated with Weak Encryption Settings or Compromised Passwords
Weak encryption settings, such as using outdated encryption algorithms or employing easily guessable passwords, dramatically increase the risk of data breaches. A compromised password, regardless of the encryption strength, provides direct access to your encrypted data. Sophisticated attackers may also utilize brute-force attacks to crack weaker encryption keys, particularly if the password is simple or the encryption algorithm is outdated.
This could lead to the exposure of sensitive personal information, financial data, or proprietary business information, resulting in significant financial and reputational damage. For example, a password like “password123” coupled with weak encryption would be easily compromised, whereas a strong, unique password combined with modern encryption significantly reduces this risk.
Regular Operating System Updates
Regularly updating your device’s operating system is paramount for maintaining strong device encryption. These updates often include crucial security patches that address vulnerabilities in the encryption algorithms and the underlying operating system itself. Failing to update leaves your device susceptible to exploits that could compromise your encryption, even if your password is strong. For instance, a known vulnerability in an older version of Android could allow a malicious app to bypass encryption and access your data.
Therefore, enabling automatic updates is highly recommended to ensure your device consistently benefits from the latest security enhancements.
Disabling or Changing Encryption Settings
Disabling or changing encryption settings should be approached with extreme caution. Disabling encryption completely removes the protection layer safeguarding your data, leaving it vulnerable to unauthorized access. Changing encryption settings, while potentially necessary in certain situations, also carries a risk of data loss if the process is not handled correctly. In some cases, altering encryption settings might require a complete data wipe and re-encryption, which would result in the loss of any unsaved data.
Therefore, disabling or changing encryption settings should only be undertaken with a thorough understanding of the implications and ideally after backing up all important data.
Best Practices for Maintaining Strong Device Encryption
Maintaining robust device encryption requires a proactive and multifaceted approach. The following best practices are recommended:
- Use strong, unique passwords for all your devices and accounts. Avoid using easily guessable passwords or reusing passwords across multiple accounts. Employ a password manager to generate and securely store complex passwords.
- Enable automatic operating system updates to ensure you always have the latest security patches installed. This helps protect against newly discovered vulnerabilities.
- Regularly back up your data to a secure location, such as an encrypted external hard drive or cloud storage service with strong encryption. This allows you to restore your data in case of accidental loss or device failure.
- Use a reputable antivirus and anti-malware program to protect your device from malicious software that could compromise your encryption or steal your data. Regularly scan your device for threats.
- Be cautious about downloading apps from untrusted sources. Malicious apps can potentially weaken your device’s security and compromise your data.
- Consider using full-disk encryption for added protection of all data stored on your device. This encrypts everything on the drive, not just specific files.
Conclusive Thoughts
Securing your device through proper encryption is a proactive step towards safeguarding your digital life. By understanding the various encryption methods available and following best practices for password management and system updates, you significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. Remember, consistent vigilance and proactive security measures are key to maintaining a secure digital environment.
Take control of your data; implement strong encryption today.